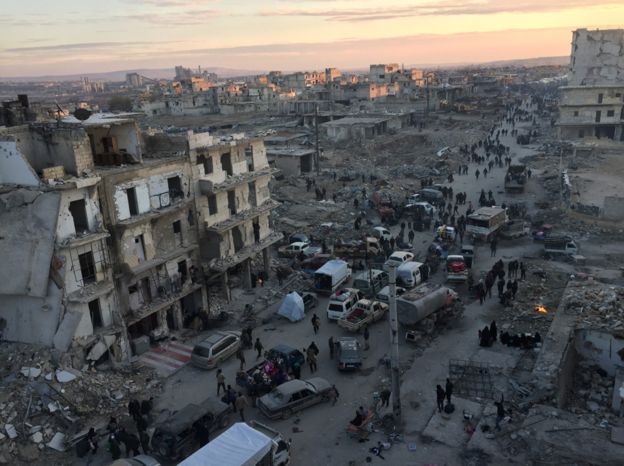
A Profile of Ahmad al-Sharaa, President of the New Syria

Tonight Donald Trump announced he will order the lifting of sanctions on Syria ‘to give them a chance at greatness’. It is a momentous declaration of confidence in the new man at the top, a man widely dismissed in the West as a religious militant, a jihadi extremist.
I am writing this post tonight because I profoundly disagree with the profiles put forward in recent months of Ahmad al-Sharaa, formerly Abu Muhammad al-Jolani, by The Economist, the Financial Times and The New York Times. They are all obsessed with his past, with his changes of direction and allegiance, with what they call his ‘chameleon’ nature. They are also convinced that he is driven by a lust for power, calling him ‘the great pretender.’
In my view, they are wrong. They misjudge and misunderstand the man, basing their analyses on the factual details they have been able to glean from various sources about al-Sharaa’s previous history and his background. They do not understand how his brain works, with some even confessing that they are puzzled by how he has managed to persuade other people to follow his directives and gain a following.
Here, I should reveal that I have an extra tool at my disposal – namely, a professional qualification in graphology earned over twenty years ago which enables me to analyse his handwriting and to see into his mind, to understand his motivations and his priorities. Handwriting is brainwriting and cannot lie. Through its subconscious elements like spacing, flow, direction, continuity, pressure and speed, it reveals the secrets of a person’s makeup, their character, their drive, their moral integrity, their strengths and weaknesses. These are elements that apply irrespective of the language or the script. I was trained on English and French handwriting, a two-year course of study with French external examiners in written and oral papers, but the same principles apply in Arabic, or indeed in any other language. Obviously when talking about a script direction being progressive, in English progressive is left to right, while in Arabic it is right to left. For regressive it is the other way round – in Arabic left to right, in English right to left.
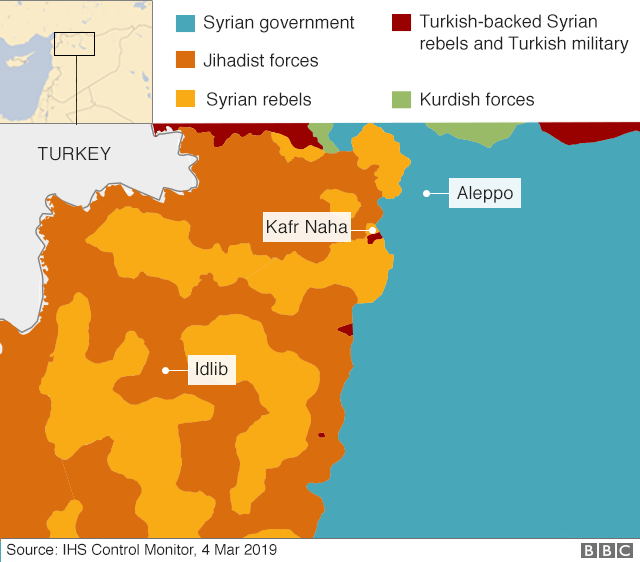
Let us look at the case of Ahmad al-Sharaa. I first saw his handwriting when it appeared online at the end of the 10 March 2025 agreement signed between him and Mazloum Abdi, commander of the SDF, the Kurdish-led Syrian Democratic Forces. The contrast between the two men’s handwriting and above all their signatures was striking.

Looking at Mazloum Abdi, his signature is not progressive, but doubles back over itself, unsure of its direction, hesitant, and ends in an unnecessary and cautious dot. Bashar al-Assad, incidentally, had a cautious, self-cancelling signature that tried to big itself up in energy-wasting flourishes that lacked direction. Some years ago I wrote a comparative analysis of Assad father and son, concluding that while Bashar might have been the face of the Assad regime, he was certainly not its backbone.
Ahmad al-Sharaa on the other hand has the most remarkable signature I have ever seen, in English or in Arabic. The sheer ingenuity and agility in the way it is formed is astonishing. It begins in the top right corner with the four Arabic letters of Ahmad – alif, Ha, mim and dal, before moving back towards the right and seamlessly becoming the letters of Ahmad in English – A, h, m, a, d. The free-flowing movement at the end of the Arabic ‘dal’ cleverly doubles as the ‘A’ of the English Ahmad. The signature then reverts to the Arabic ‘al-‘ of the start of his family name, before ending in a final progressive flourish where the letters of Sharaa are not legible. There are four changes of direction, and the pen never leaves the paper. It is all one smooth stroke, carried out at speed. The movements throughout are highly progressive, never regressive. This is a man who only moves forwards, never backwards, and who is always open to all manner of solutions, approached from a variety of angles. He thinks outside the box and shows great adaptability and flexibility, whilst remaining true to his own vision. He is not driven by greed for power or money, but rather by a genuine belief that he has the ability to bring Syria forward into a new and progressive future. He is not dogmatic, stubborn or difficult.

His writing illustrates clearly the complex journey he has been on in his life to arrive at where he is now. His many changes of direction have been integral and necessary parts of his life. A signature of this complexity has taken many years to evolve, and certainly did not suddenly appear on 8 December 2024 with the fall of Assad. It is not just pragmatism, as western analysts like to describe it. It is far more than that. It is his ability to adapt quickly to changing situations and to move progressively with the flow of events as they unfold. This is a skill that requires deep intelligence, thoughtfulness and good judgement combined, all exercised simultaneously and at pace. On top of that there is also an element of playfulness and humour, making him likeable and popular. The New Syria would be hard pushed to find a better man to navigate the challenging road that lies ahead.